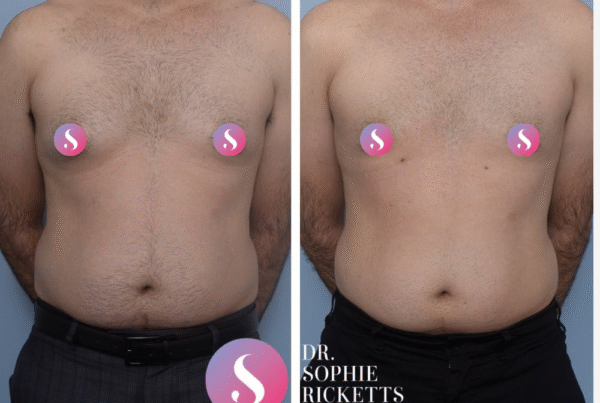
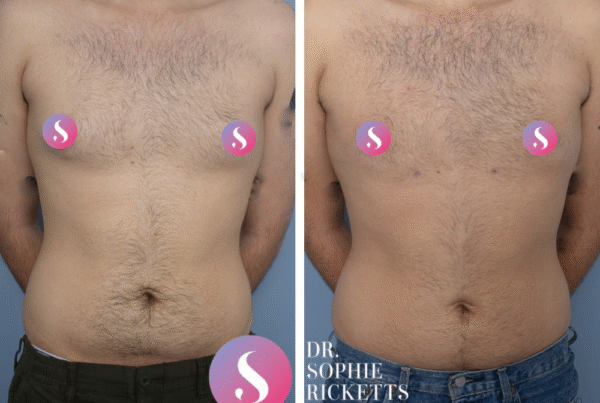
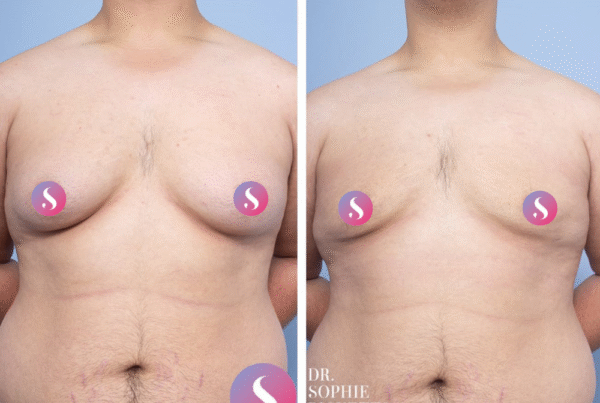
Male Breast Surgery (Gynaecomastia)
Why might gynaecomastia surgery be considered?
Gynaecomastia is a clinical condition characterised by the enlargement of glandular breast tissue in males. While it is usually benign and often has no identifiable cause, it can result from an imbalance between the hormones testosterone and oestrogen. Surgery, or male breast reduction, is considered when the enlargement is persistent and does not resolve with the treatment of underlying medical causes.
The Surgical Approach
The procedure typically involves a combination of liposuction to remove excess fat and surgical excision to remove firm glandular tissue often directly below the nipple. In cases with significant skin laxity, a skin reduction may also be required.
During a consultation, Dr Ricketts will perform a clinical assessment to determine the underlying cause and ensure there are no contraindications to surgery. It is a mandatory requirement under AHPRA guidelines that patients undergo a formal GP referral and a cooling-off period before proceeding with elective cosmetic surgery.
How is the surgery performed?
Surgical management of gynaecomastia often involves liposuction to remove fatty tissue. If firmer glandular tissue remains after liposuction, this may be removed through an incision at the border of the areola. In some cases where the skin does not contract adequately, skin removal may also be considered. The surgical approach depends on each individual’s anatomy and circumstances and will be discussed during consultation.
Will there be scars?
Gynaecomastia surgery is a clinical procedure performed to address the enlargement of male breast tissue. It typically involves the removal of persistent glandular tissue and excess adipose (fatty) tissue that has not responded to conservative management. If glandular tissue or skin requires removal there will be scars, either on the edge of the nipple or sometimes on the skin of the chest.
Key Clinical Aspects:
- Surgical Techniques: Specialist Plastic Surgeon Dr Sophie Ricketts typically utilises liposuction to remove fat and surgical excision to remove firm glandular tissue. If significant skin laxity is present, a skin reduction may also be required.
- Incisions and Scars: All surgery results in permanent scars. Most incisions are placed in a semi-circle around the lower border of the areola. If a larger skin reduction is necessary, incisions may extend across the chest.
- Scar Maturation: Scars generally take 12 to 18 months to soften and fade. Adherence to post-operative scar management, such as silicone therapy, is essential for optimal maturation.
- Recovery: Patients must wear a medical-grade compression vest for several weeks post-surgery to manage swelling and support the new chest contour. Strenuous upper-body exercise is restricted for approximately six weeks.
What is the recovery process?
Gynaecomastia surgery is typically performed as a day procedure under general anaesthesia. While most patients return home the same day, the total recovery period involves several distinct stages of tissue healing and maturation.
Immediate Post-Operative Phase (Week 1–2)
- Compression Garment: You must wear a medical-grade compression vest 24/7 for the first 2–4 weeks. This is a clinical requirement to minimise haematoma (internal bleeding), manage swelling, and ensure the skin adheres correctly to the new chest contour.
- Activity Levels: You should remain mobile with gentle walking, but you must avoid any lifting (typically over 5kg) or strenuous activity.
- Driving: You may return to driving once you have ceased prescription pain medication and have a comfortable range of motion, usually after 7 to 10 days.
Intermediate Recovery (Week 3–6)
- Swelling and Bruising: Initial swelling and bruising generally resolve within the first three weeks. However, swelling can persist for several months.
- Exercise: Light cardiovascular exercise may typically resume at week three. However, chest-specific exercises (such as bench presses or push-ups) and high-impact activities must be avoided for 6 weeks.
Long-Term Maturation (3–12 Months)
While the primary results are visible early on, the final chest contour and scar maturation can take up to one year. During this time, the internal tissues soften and the scars fade from pink to a pale, flat line.
Clinical Follow-Up
Specialist Plastic Surgeon Dr Sophie Ricketts will monitor your progress through a series of scheduled appointments. These are mandatory to ensure your incisions are healing correctly and to provide clinical clearance for the gradual return to full physical activity.
Gynaecomastia Surgery: Risks and Complications
Gynaecomastia surgery (male breast reduction) is a significant surgical undertaking. Dr Sophie Ricketts prioritises clinical risk management and comprehensive informed consent; therefore, it is essential to understand the potential complications associated with this procedure before deciding to proceed.
General Surgical Risks
-
Anaesthesia Complications: Risks associated with general anaesthesia, including allergic reactions or respiratory issues.
-
Haematoma and Seroma: The accumulation of blood (haematoma) or clear fluid (seroma) under the skin, which may require surgical drainage.
-
Infection: Post-operative infection may require antibiotic treatment or, in rare cases, further surgery.
-
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): The risk of blood clots in the legs, which can be life-threatening if they travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
-
Poor Wound Healing: Risks are higher for patients who smoke or have certain underlying health conditions.
Specific Risks of Gynaecomastia Surgery
-
Nipple and Skin Sensation Changes: Temporary or permanent numbness or altered sensitivity in the nipples or chest skin.
-
Asymmetry: Variations in healing or underlying chest wall structure may result in differences between the two sides of the chest.
-
Contour Irregularities: The treated area may appear uneven or have “dents” or ripples, particularly if skin elasticity is poor.
-
Nipple Necrosis: In rare cases, the blood supply to the nipple may be compromised, leading to partial or total loss of the nipple/areola tissue.
-
Excess Skin: If the skin does not contract sufficiently after fat or tissue removal, additional surgery may be required to remove redundant skin.
-
Internal Scarring (Fibrosis): Hardness or “lumpiness” under the skin caused by internal scar tissue.
-
Unsatisfactory Aesthetic Result: The risk that the final shape or contour does not meet expectations.
Long-Term Considerations
-
Recurrence: Gynaecomastia can recur if there is significant weight gain, use of certain medications, or the use of anabolic steroids/recreational drugs.
-
Need for Revision Surgery: Approximately 3–5% of patients may require a secondary procedure to refine the result or address complications.
Gallery
Individual results vary. All surgical procedures carry risks and require a consultation to determine suitability.
These images are for illustrative purposes only and do not guarantee a specific outcome. Before proceeding, you should seek a second opinion from an appropriately qualified health practitioner.
FAQ
What is gynaecomastia?
Gynaecomastia is a clinical condition characterised by the enlargement of male breast tissue. There is typically no cause found but can be caused by a hormonal imbalance—specifically an increase in oestrogen or a decrease in testosterone—which results in the growth of glandular tissue rather than simple adipose (fat) tissue. It can also be caused by recreational steroid use.
Factors contributing to gynaecomastia may include:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Naturally occurring changes during puberty or ageing.
- Medication side effects: Reactions to certain prescription drugs or substances.
- Genetics and underlying health conditions: Structural changes necessitated by individual physiology.
How is the condition managed?
A formal clinical assessment is required to determine the underlying cause and whether surgical intervention is appropriate. Gynaecomastia surgery (male breast reduction) is a surgical option intended to reduce the volume of fatty and glandular breast tissue and contour skin.
As with all surgical procedures:
- A GP referral is mandatory before an initial consultation can take place.
- Two consultations and a 7-day cooling-off period are required before booking.
- Psychological screening for Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) is a standard part of the assessment process.
Results vary significantly between individuals, and all surgery carries inherent risks.
How common is gynaecomastia in men?
Gynaecomastia is a frequent clinical finding, affecting an estimated over 50% of the male population at different life stages. It is defined as a benign enlargement of the glandular breast tissue in males.
Common Clinical Presentations:
- Puberty: Approximately half of adolescent males experience transient tissue enlargement due to hormonal shifts. In most cases, this resolves spontaneously within two years.
- Older Age: Prevalence increases in men aged 50–80 as testosterone levels naturally decline relative to oestrogen.
- Medical Triggers: The condition can also be linked to certain medications, underlying health conditions, or lifestyle factors.
While often painless, some individuals experience mastodynia (breast tenderness) or physical discomfort. When gynaecomastia is persistent and does not respond to conservative management, a consultation with Specialist Plastic Surgeon Dr Sophie Ricketts may be appropriate to discuss surgical options.
At what age does gynaecomastia usually occur?
Gynaecomastia (male breast enlargement) typically occurs during three distinct life stages, primarily driven by fluctuations in the balance between testosterone and oestrogen.
Key Life Stages:
- Infancy (Neonatal): Affects up to 90% of male newborns due to maternal hormones; it typically resolves within weeks.
- Adolescence (Pubertal): Peak onset occurs between ages 12 and 15, affecting approximately half of all teenage boys. In the vast majority of cases, the tissue regresses naturally within two years as hormonal balance is achieved.
- Older Adulthood: Prevalence increases significantly between ages 50 and 80 due to age-related testosterone decline, changes in body composition, or the side effects of certain medications.
Clinical Path Forward
Surgery is generally only considered for “persistent” gynaecomastia—tissue that has remained stable for 12 to 24 months and has not responded to conservative management or the removal of triggering factors. Specialist Plastic Surgeon Dr Sophie Ricketts requires a GP referral to assess the underlying cause before discussing surgical options.
Can gynaecomastia affect both breasts or just one?
In clinical practice, gynaecomastia can present as either bilateral (affecting both breasts) or unilateral (affecting just one). It is also common for the condition to be asymmetrical, where both sides are involved but to varying degrees of enlargement. Dr Sophie Ricketts, a specialist in treating this condition, often evaluates whether the enlargement is symmetrical and advises on the most suitable management options, including surgery if required.
Who is a good candidate for a male breast reduction?
A suitable candidate for male breast reduction is someone whose condition is medically stable and who meets the health requirements for elective surgery in Australia. Under AHPRA guidelines, surgery is viewed as a clinical intervention for persistent tissue enlargement rather than a lifestyle choice.
Key Clinical Requirements:
- Persistence of Condition: The glandular tissue must have remained stable for at least 12 to 24 months without regressing naturally.
- Health and Lifestyle: Candidates must be in good general health for general anaesthesia. Being a non-smoker is essential, as nicotine significantly increases the risk of wound complications and tissue necrosis.
- Weight Stability: A stable, healthy weight is required to ensure the long-term integrity of the surgical contour.
- Informed Consent: Candidates must have a realistic understanding of surgical outcomes, including the maturation of permanent scars.
When is surgery recommended for gynaecomastia?
Surgical intervention, known as a male breast reduction, is typically considered only after a thorough clinical investigation into the underlying cause of the glandular enlargement. It is generally reserved for cases where the condition is “persistent” and non-surgical pathways have been exhausted.
- Clinical Timing and Criteria
Tissue Stability: Surgery is generally only considered once the glandular tissue has been stable for at least 12 to 24 months. This is particularly important for pubertal gynaecomastia, as most cases resolve spontaneously once hormonal balance is achieved. - Failure of Conservative Management: If the enlargement is linked to specific medications, health conditions, or lifestyle factors, these must be addressed first. Surgery is an option only if the tissue remains unchanged after these triggers are removed.
- Physical Symptoms: Surgery may be clinically indicated if the enlargement causes mastodynia (physical pain or tenderness) or significant physical discomfort during daily activities.
- Skin Elasticity: In cases where significant weight loss has occurred, the presence of redundant, inelastic skin may necessitate surgical removal to restore a functional chest contour.
Regulatory Requirements
Before undergoing surgery in Australia, there are several mandatory clinical steps:
- GP Referral: You must obtain a referral from your General Practitioner. This ensures that systemic causes—such as liver, kidney, or endocrine disorders—have been medically investigated.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Specialist Plastic Surgeon Dr Sophie Ricketts often requires a breast ultrasound to distinguish between glandular tissue (gynaecomastia) and adipose tissue (pseudogynaecomastia).
- Cooling-Off Period: A mandatory 7-day cooling-off period is required between your initial consultation and the signing of a consent form to ensure an informed, unpressured decision.
Long-Term Considerations
Surgery provides a long-term solution by physically removing the glandular tissue. However, to maintain the clinical result, patients must maintain a stable weight and avoid medications or substances that could trigger a recurrence of hormonal imbalance.
Is gynaecomastia the same as having excess chest fat?
No. While they may appear similar, gynaecomastia and pseudogynaecomastia are distinct clinical conditions involving different types of tissue. Understanding the difference is critical for determining the appropriate clinical management.
Gynaecomastia (Glandular Growth)
True gynaecomastia is the proliferation of glandular breast tissue in males.
- Cause: It is primarily driven by an imbalance between testosterone and oestrogen.
- Characteristics: The tissue typically feels firm or rubbery and is often located directly behind the nipple-areolar complex. It may be associated with mastodynia (tenderness).
- Management: Glandular tissue is permanent and does not respond to diet or exercise. If conservative monitoring fails, surgical excision is usually required.
Pseudogynaecomastia (Adipose Tissue)
Pseudogynaecomastia is the accumulation of subcutaneous adipose tissue (fat) in the chest area without glandular enlargement.
- Cause: It is generally associated with overall weight gain or individual genetic fat distribution.
- Characteristics: The tissue feels soft and is usually distributed more broadly across the chest wall rather than concentrated behind the nipple.
- Management: This condition may resolve or improve significantly with weight loss and targeted physical activity.
Clinical Assessment
In many cases, a patient may present with a combination of both glandular and fatty tissue. Specialist Plastic Surgeon Dr Sophie Ricketts will perform a physical examination and may request a breast ultrasound to confirm the ratio of gland to fat. This assessment is necessary to determine if liposuction, surgical excision, or a combination of both is required for your anatomical goals.
What is the recovery like after male breast reduction surgery?
Recovery after male breast reduction varies between individuals. A compression garment is usually worn after the procedure to support the area and help manage swelling. Bruising, swelling and discomfort are common in the early stages and generally change over the first few weeks.
More strenuous activity is often limited for a period of time, while light activity such as walking may be appropriate earlier, depending on your surgeon’s advice.
Scarring depends on the technique used. When liposuction alone is performed, the incisions are small. If glandular tissue is removed through an incision at the edge of the areola, the scar in that area generally becomes less noticeable over time, although the appearance of scars varies between individuals.
Your surgeon will provide postoperative instructions based on your individual circumstances and the extent of your surgery.